
Thinking fast and slow
Why read this
You should read this book, if you are interested to learn about cognitive biases. It is filled with decades of research and examples where you will notice your biases in play. There were some studies which failed to replicate in recent experiments.
Overall, its great for introduction to Behavioral Economics.
5 key take-aways
- The biggest takeaway is that we are not rational all the times.
- We are unaware of cognitive biases most of the times.
- Luck plays a crucial role in life.
Summary
Introduction
Biases are systematic errors in thinking.
Halo effect -> Handsome speaker are judged favorably than he deserves.
How do thoughts arise
The mental work that produces impressions, intuitions, and many decisions goes in silence in our mind.
Media and bias
People tend to assess the relative importance of issues according to the ease with which they were retrieved. THus, Media coverage determines the importance of issue.
" It is no accident that authoritarian regimes exert substantial pressure on independent media”
Chess players developed intuition after playing chess for thousands of hours.
Affect heuristic: The executive’s decisions could be guided by liking and disliking with little deliberation or reasoning.
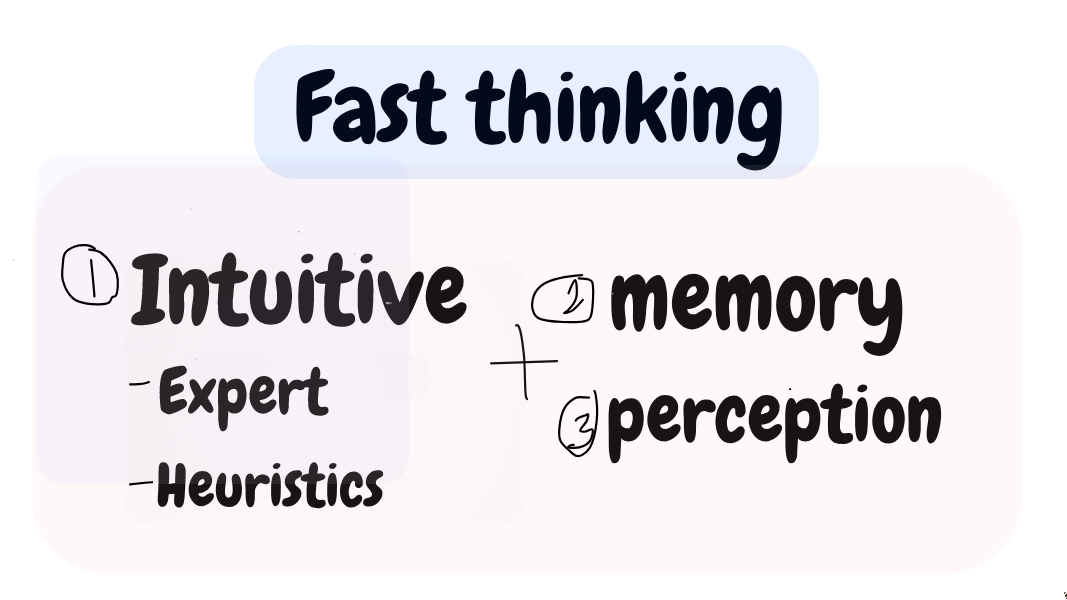
What is fast thinking
Fast thinking involves these intuitive thoughts and and also the automatic mental activities of perception and memory.
System 1 and System 2
System 1 is fast thinking. System 2 is slow thinking.
Role of luck
We are prone to overestimate how much we understand about the world and underestimate the role of chance (randomness, luck)
A reoccurring theme is that luck plays an important role in every story of success.
Two Systems
System 1 and system 2 are analogies and not real systems.
How do we Identify ourselves?
When we think of ourselves, we identify with System 2, the conscious, reasoning self that has beliefs, makes choices, and decides what to think about and what to do.
Intense focusing makes a person effectively blind to even to a stimuli that attracts normal attention.
Cognitive Illusions
Cognitive illusions are illusions of thought or called biases.
Attention and Effort
More skilled in a task -> less demand for energy.
Effort is required to maintain simultaneously in memory several ideas that require separate actions, or that need to be combined according to a rule
- rehearsing your shopping list as you enter the supermarket,
- choosing between the fish and the veal at a restaurant
What is task sets
System 2 Can program memory to override habitual response with another instruction.
People who do better on working memory tests -> do well on tests of general intelligence.
However, ability to hold attention is not simply a measure of intelligence.
Time pressure is another driver of effort.
How to avoid mental overload
- Divide the tasks into simple steps.
- Note: Similar to GTD system by David Allen.
- Commit intermediate results to memory or paper.
3 - The Lazy Controller
Maintaining coherent train of thoughts and occasional engagement in effortful thinking also requires self-control.
Law of least effort
Frequent switching of tasks and speeded up mental works are not intrisically pleasurable so people tend to avoid them.
Cognitive work is not aversive (a feeling of intense dislike).
“Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi describes the state of flow which is the a state of effortless concentration so deep that they lose their sense of time, of themselves, of their joy and problems.”
Flow requires
- Concentration on the task
- Deliberate control of attention,
System 2 and business
System 1 has more influence on behavior when System 2 is busy or depleted,
When System 2 is depleted, you are more likely to speak swear words, make sexist comments.
Too much concern about how well one is doing in a task sometimes disrupts the performance by loading short term memory with pointless anxious thoughts


